Content
- Linguistic resources of the referential function
- Examples of sentences with referential function
- Language functions
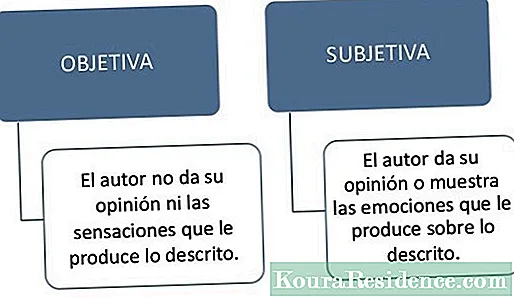
The referential function It is the function of language that is used to convey objective information about everything that surrounds us: objects, people, events, etc. For example: The capital of France is Paris.
The referential function, also called the informative function, focuses on the referent (the topic that is being discussed) and the context (the situation in which it is discussed). It is used to convey objective information, that is, without making assessments and without seeking a reaction from the listener.
It is the main function of language since it can refer to anything. Even when another function is the main one, the referential function is usually present. For example, if we use the expressive function to convey our admiration for a person's beauty, we will inevitably convey some kind of objective information about their traits or characteristics.
It is the most used function in informative, journalistic and scientific texts, although it can also be used in literary fiction or essay texts, combined with other functions of language.
- It can serve you: Expository text
Linguistic resources of the referential function
- Denotation. In the referential function it is more common for words to be used in the denotative sense, that is, it is the primary meaning of the words that is opposed to the connotation, which is the figurative sense. For example: The new president of Mexico is from a left party.
- Nouns Y verbs. Nouns and verbs are the most used words in this function as they allow you to convey objective information. For example: The house is for sale.
- Declarative intonation. A neutral tone characteristic of affirmative or negative sentences is used, without exclamations or questions. For example: The team came out last.
- Indicative mode. Verbs are mainly conjugated in the various tenses of the indicative mood. For example: The show starts at eight.
- Deictics. They are words that are interpreted in relation to the communication situation and context. For example: This project was rejected.
Examples of sentences with referential function
- The arrival of the national team to Venezuela will take place on Sunday night.
- The young man is 19 years old.
- It will be ready for next Monday.
- The window did not break without anyone seeing what had happened.
- The delivery was not scheduled for today.
- The bread was in the oven.
- The media described the event as "massive."
- The fault cannot be fixed.
- Three days later, he discovered that the mistake had been his.
- The prices of this trade are 10 percent more expensive than ours.
- The father had fallen ill.
- He's been sleeping for three hours.
- The coffee is ready.
- The dogs barked for hours.
- This is the tallest tree.
- The box is empty.
- Those fish no longer exist.
- He asked her why she hadn't called him.
- There are five different options to choose from.
- His brothers did not find out what happened.
- The island is 240 kilometers long and a maximum of 80 kilometers wide.
- They are my brothers.
- The plane is about to take off.
- The capital of France is Paris.
- Food is insufficient for three children.
- The celebration continued until 11 pm.
- Two years had passed when they saw him again.
- The phone didn't ring all morning.
- He dyed his hair blonde.
- He designed the dresses for the wedding.
- Isaac Newton died in 1727.
- The failure was not what you expected.
- The children played on the terrace.
- This is the most expensive project of all.
- The trade opens in an hour.
- As soon as he entered the house, food was prepared.
- This model was the least sold in the whole country.
- This year I visited three different countries.
- Breakfast is served on the ground floor.
- He will return today at five in the afternoon.
- Someone rang the bell and then ran off.
- There is no one left in the house.
- The chair has stains.
- The locals came out to enjoy the sun.
- The disinfectant smell will dissipate in a few hours.
- He called him five minutes before seven in the afternoon.
- A dog slept by the door.
- The film opened on Thursday.
- We are at the highest point of the mountain.
- There are alternative paths.
- They painted the closet white.
- They stated that they knew nothing of the matter.
- Orange trees are the most common trees in this area.
- He said he needed another pair of shoes.
- The door is open.
- Before I go shopping, I'm going to finish cleaning the house.
- There are no more shoes in that size.
- Lunch will be served at nine o'clock.
- The whole family has gathered in the garden.
- I'll be here twenty minutes later.
- Juan arrived five minutes later than Pablo.
- The wedding is next Saturday.
- The board is made up of five people.
- The train always arrives on time.
- Neurons are part of the nervous system.
- That dress is discounted.
- He didn't remember her name.
- All the exercises were solved correctly.
- We agree with the decision made.
- In that corner is the premises.
- Felipe III was a king of Spain.
- Peru's capital is Lima.
- Half of the furniture was broken.
- One hundred and five people surveyed said they were very touched.
- This room measures thirty square meters.
- Jamaica is located in the heart of the Caribbean Sea, 150 kilometers south of Cuba.
- This chocolate does not contain sugar.
- Across the river was a path that led to a house he had never visited.
- This is the closest police station.
- The professor paid no attention to them.
- This was his first match.
- It won't rain for another two weeks.
- Nobody knows us in this town.
- Last night at eight at night.
- There was nothing left to eat in the kitchen.
- The suspect denied all allegations.
- He told her that he liked the theater and painting.
- No one at the club admitted knowing him.
- His house has a garden.
- We are twenty kilometers away.
- Behind the house there is a garden.
- This is the second street we cross.
- The temperature dropped three degrees since the morning.
- The car is five years old.
- Ten people saw him leave the house.
- Half an hour left to take the exam.
- You can choose the color you prefer.
- The pencil is broken.
- There are no free seats.
- The songs were his own.
Language functions
Linguists studied the way we speak and found that all languages change their form and function depending on the purpose for which they are used. In other words, every language has different functions.
Language functions represent the different purposes that are given to language during communication. Each of them is used with certain objectives and prioritizes a certain aspect of communication.
- Conative or appellative function. It consists of inciting or motivating the interlocutor to take an action. It is centered on the receiver.
- Referential function. It seeks to give a representation as objective as possible of reality, informing the interlocutor about certain facts, events or ideas. It is focused on the thematic context of communication.
- Expressive function. It is used to express feelings, emotions, physical states, sensations, etc. It is centered on the issuer.
- Poetic function. It seeks to modify the form of language to provoke an aesthetic effect, focusing on the message itself and how it is said. It is focused on the message.
- Phatic function. It is used to start a communication, to maintain it and to conclude it. It is centered on the canal.
- Metalinguistic function. It is used to talk about language. It's code-centric.