Author:
Peter Berry
Date Of Creation:
19 February 2021
Update Date:
15 May 2024
Content
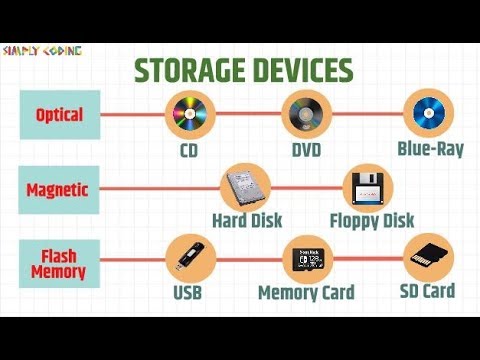
Thestorage devices Data are the components of a computer system that have the role of transmitting or retrieving digital information (Record Y read) on various physical supports created for it.
They should not be confused with the data storage medium or data storage medium, terms that refer precisely to the physical vehicle of the information, whether handled by a computer or by a device of another nature.
Data storage devices can be:
- Primary: Those necessary for the operation of the system as they contain vital metadata to start the OS.
- Secondary: Those accessories, removable or not, with which it is possible to enter and extract data from and to the system.
They can serve you:
- Examples of Peripherals (and their function)
- Examples of Input Devices
- Examples of Output Devices
- Examples of Mixed Peripherals
Examples of storage devices
- RAM:Acronym for Random Access Memory (Random Access Memory), is the storage field used as a working medium in computer systems, as it contains all the processor instructions and most of the processor instructions. software. Shutting down or restarting the system erases all of its content.
- ROM memory:Acronym for Read-Only Memory (Read Only Memory), is a storage medium that contains data that is difficult (or impossible) to modify, vital for the basic functioning of the computer system and its primary operating system.
- Magnetic tape cassettes (DAT):These are systems for recording and reading digital audio information, which handle small devices or plastic cassettes with magnetic tape inside, which operate similarly to their analog cousins.
- Digital Magnetic Tape Devices (DDS):Derived from DAT systems, they are digital and computerized information management units made from magnetic tape, remotely similar to the VHS format.
- 3½ floppy drives (obsolete):Evolution of the floppy disk drive, these drives used more rigid and durable floppy disks, with higher capacity (1.44 MB).
- Rigid or "Hard" Disk Drives:Known as HDD (Acronym for Hard Disk Drive), are units with much larger storage than optical discs and memories, but they are usually found inside the CPU and are not removable. That is why they usually contain the information of the operating system and the content of files and computer software in their entirety.
- Portable Hard Drives:Removable and external version of the hard disk, they connect to the computer through its I / O ports and hold large amounts of information.
- CD-ROM drives:Acronyms for Compact Disc Read-Only Memory (Compact Disc Read Only Memory), are read only devices created in 1985 and that operate based on a laser beam that, reflected on the sheet inside the disc, supplies the computer with a set of binary signals from the plains and crevices of it.
- CD-R / RW drives:Similar to the CD-ROM, these drives allow not only the reading but also the partial or definitive writing of compact optical discs, in some cases allowing their reuse.
- DVD-ROM drives:Acronyms for Digital Versatile Disc (Digital Versatile Disc), operates in a similar way to CD, that is, it is recorded only once and can be read many times, but with the difference that it supports up to 7 times the information load of these formats.
- DVD-R / RW drives:These are DVD disc burning and rewriting drives, allowing up to 4.7 Gigabytes of information to be written to them.
- Blue Ray Units:This is the name given to a new generation optical disc format, endowed with much greater storage capacity and reading quality, since the laser used for this reading is blue instead of the traditional red. Supports up to 33.4 Gigabytes per recording layer.
- Zip Units:Introduced to the market in the mid-1990s, ZIP drives operate from high-capacity magnetic disks, from peripheral units. They were replaced by flash memories.
- Flash Memory Drives:Connected to the computer via USB or Firewire, these readers allow the support of information in a portable format compatible with digital cameras and electronic agendas.
- Memory Card Units:Like flash memory (arguably a form of it), portable memory devices or memory cards allow large-scale physical handling of information through USB ports. There is a huge variety of models, known as Pendrive since some have the practicality of a ballpoint pen.
- Punch Card Unit (Obsolete):This technology consisted of information reading systems from cardboard cards that were made a hole in a certain place, to allow optical reading of the binary code: hole represented one value (1), without hole represented another (0) .
- Punched Tape Drive (Obsolete):Similar to punch cards in operation, they went a step further, turning the cardboard cards into a long instructional tape, allowing for much more information to be handled.
- Magnetic drums (obsolete):One of the first forms of memory for computers, invented in 1932, stored information in layers of iron oxide through rotating metals that, although not removable, allowed information to be retrieved at high speeds.
- Cloud storage:The development of online storage systems and high data transmission speeds on the Internet have made it possible to use it as a reading and writing device, so many entrust their files to "the cloud" instead of to physical media .
Follow with:
- Examples of Peripherals (and their function)
- Examples of Input Devices
- Examples of Output Devices
- Examples of Mixed Peripherals